
Art Gharana — 12 Mins read
Complete Guitar Strings Guide (Electric & Acoustic)
Musical Instruments
Have you ever wondered what gives brass instruments their bold, brilliant sound that can fill a concert hall or energize a marching band? From the piercing call of the trumpet to the deep resonance of the tuba, brass instruments have shaped music across centuries, blending power, precision, and passion. These wind instruments, known as Aerophones, produce sound through air vibration created by the player’s lips — a fascinating process that turns simple breath into breathtaking music.
Each member of the brass family carries its own charm and challenge, defined by unique valves and slides, intricate Embouchure control, and the shimmering quality of metal alloy construction. Whether in a baroque orchestra or a modern jazz ensemble, these lip-vibrated instruments continue to evolve, offering endless opportunities for creative musical expression.
In this blog, we’ll take you on a journey through the different types of brass instruments, exploring their history, mechanics, and playing techniques. You’ll not only discover what makes each instrument special but also gain insights into how they contribute to the grand orchestral brass section. So, if you’ve ever been curious about how these timeless musical instruments transform air into art — you’re about to find out.
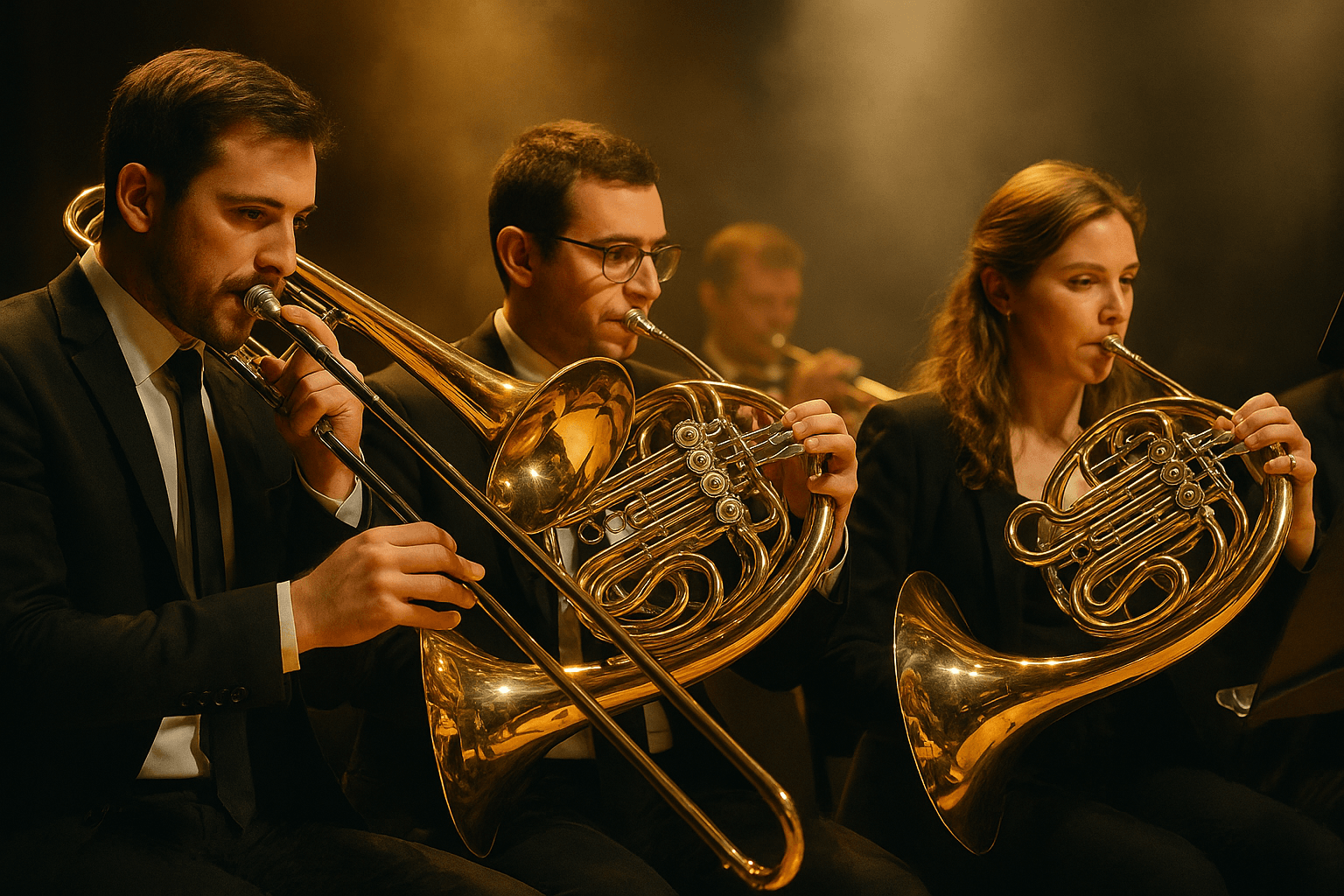 What makes brass instruments so captivating that they’ve stood the test of time, shaping centuries of music performance? Whether it’s the triumphant blare of a trumpet or the warm hum of a French horn, each sound begins with something simple — air vibration. Yet, what happens next is pure magic.
What makes brass instruments so captivating that they’ve stood the test of time, shaping centuries of music performance? Whether it’s the triumphant blare of a trumpet or the warm hum of a French horn, each sound begins with something simple — air vibration. Yet, what happens next is pure magic.
Brass instruments, also known as Aerophones, belong to a special category of wind instruments where sound is created by the player’s lips “buzzing” against a mouthpiece. This lip vibration — or Embouchure — sends waves through a cylindrical chamber, transforming breath into bold, resonant tones. The control of air flow and pressure determines pitch, volume, and tone, allowing musicians to express everything from gentle melodies to powerful fanfares.
To truly understand the soul of brass, let’s break down what defines them:
Material: Typically made from a metal alloy like brass or bronze, which enhances resonance and projection.
Structure: A long, coiled tube ending in a flared bell that amplifies sound.
Mechanics: Uses valves and slides to alter the tube’s length and control pitch.
Sound Production: Created by the interaction between air vibration, mouthpiece pressure, and Embouchure precision.
Each of these elements plays a vital role in shaping the distinct voices within the brass instruments list, from the mellow euphonium to the heroic trombone.
What’s fascinating about brass instruments is how sound production merges art and physics. The harmonic scale produced by each instrument depends on how the player manipulates tuning slides and air pressure. A small change in Embouchure can completely transform the tone — proving that mastering a brass instrument is as much about technique as it is about feeling.
Whether you’re drawn to their majestic presence in an orchestral brass section or curious about how they enrich modern bands, brass instruments are the bridge between raw breath and refined beauty.
If exploring these instruments excites you, you can take the first step by joining an Online Instrument Course or even book a trial class to experience the sound firsthand.
 Few brass instruments can rival the brilliance and energy of the trumpet. Its piercing clarity and rich timbre have made it a favorite across genres — from the regal fanfares of the baroque period to the soul-stirring solos of modern jazz. But what makes the trumpet so iconic in the world of musical instruments?
Few brass instruments can rival the brilliance and energy of the trumpet. Its piercing clarity and rich timbre have made it a favorite across genres — from the regal fanfares of the baroque period to the soul-stirring solos of modern jazz. But what makes the trumpet so iconic in the world of musical instruments?
The secret lies in its sound production. The player’s lips vibrate against a small mouthpiece, setting the air vibration in motion through a slender cylindrical chamber. The length of the tubing, combined with precise Embouchure control, determines the pitch and tone. Add to that the trumpet’s valves and slides, which adjust the airflow path, and you have an instrument capable of extraordinary pitch control and tonal diversity.
The history of the trumpet stretches back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations used primitive versions like the fanfare trumpet and medieval trumpet to signal kings, armies, or ceremonies. By the baroque period, the trumpet had evolved into a sophisticated instrument central to orchestras and royal courts. Today, advancements like piston valves and rotary valves allow for smoother transitions between notes and richer harmonics.
Let’s explore why the trumpet continues to capture hearts and stages worldwide:
Versatility – From classical orchestras to pop and jazz, the trumpet adapts beautifully to any style.
Expressive Range – Its bright, brassy voice can soar above an ensemble or whisper with soulful emotion.
Technical Mastery – Mastering Embouchure and breath control unlocks the full harmonic scale potential.
Compact Design – Despite its small size, the trumpet produces one of the most powerful sounds in the brass instruments list.
Over time, legendary performers like Wynton Marsalis, Arturo Sandoval, and Ambrose Akinmusire have redefined trumpet performance, demonstrating its ability to convey passion, precision, and personality. Their work showcases how an instrument rooted in tradition continues to evolve with modern musical expression.
If you’re inspired to explore instruments, consider joining an Online Instrument Course to learn the techniques behind this dynamic art form. You can even book a trial class and experience the thrill of playing your first note.
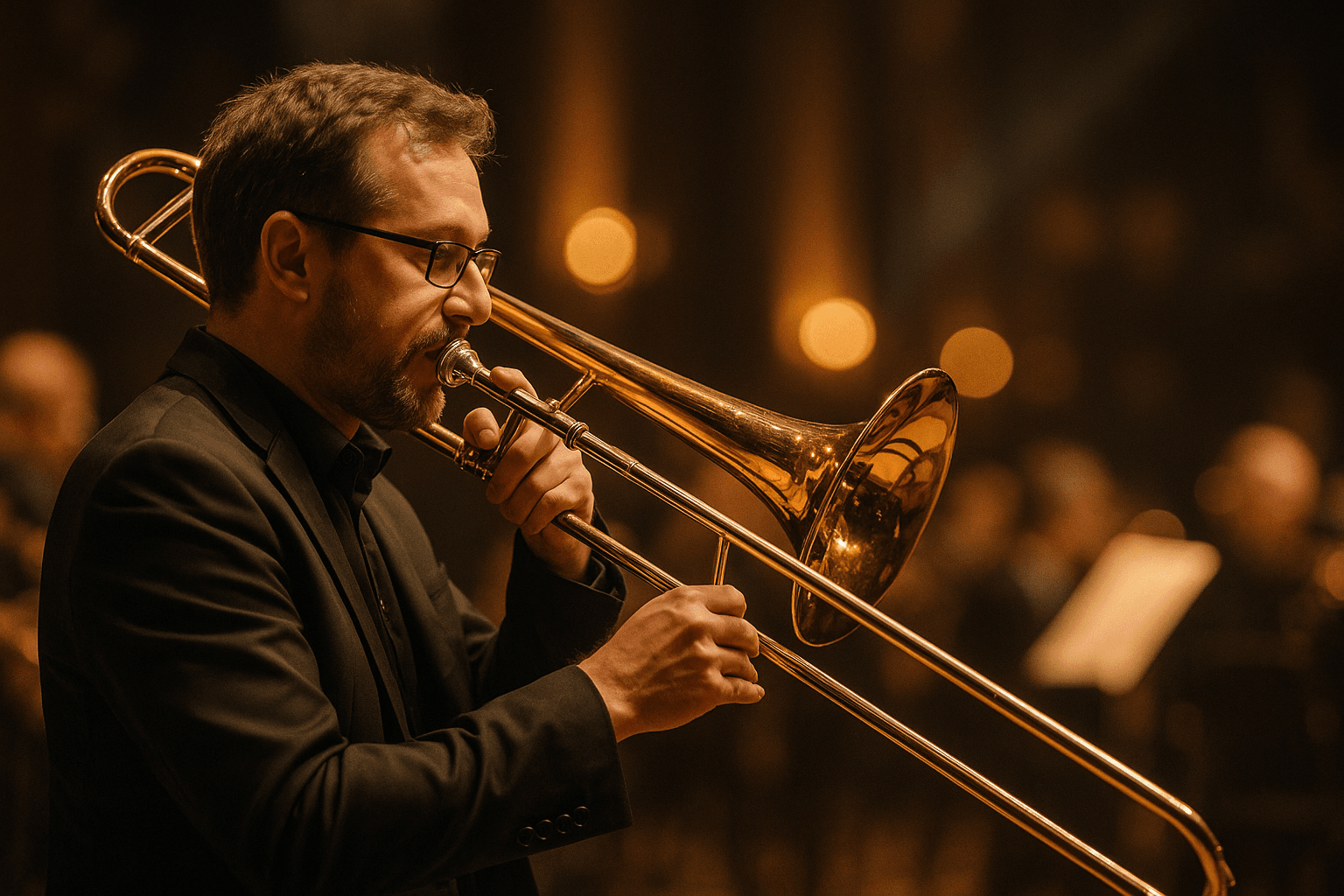 Have you ever noticed how the trombone stands out in a brass instruments list — not just for its sound but for the way it’s played? Unlike other brass instruments that rely on valves, the trombone uses a slide mechanism to change pitch, giving it a unique blend of power, precision, and playfulness. It’s the only brass instrument that moves seamlessly between notes, producing smooth glissandos that make it instantly recognizable in both orchestras and jazz bands.
Have you ever noticed how the trombone stands out in a brass instruments list — not just for its sound but for the way it’s played? Unlike other brass instruments that rely on valves, the trombone uses a slide mechanism to change pitch, giving it a unique blend of power, precision, and playfulness. It’s the only brass instrument that moves seamlessly between notes, producing smooth glissandos that make it instantly recognizable in both orchestras and jazz bands.
At its core, the trombone’s magic lies in its mechanics. The player’s Embouchure (lip control) and air flow create air vibrations within the cylindrical chamber, while the slide adjusts the instrument’s length to modify pitch. The longer the slide is extended, the lower the pitch becomes. This direct manipulation gives trombone players incredible pitch control and expressive freedom that few other wind instruments can match.
Over time, the trombone has evolved into several distinct versions — each suited to different musical settings:
Each version carries its own charm, yet all share the same hallmark: a warm, resonant tone and the ability to shift effortlessly between registers.
From bold orchestral themes to soulful jazz solos, the trombone adds emotional depth wherever it appears. Its signature slides — or “smears” — make it perfect for expressive tone variation, while techniques like trills and overblowing allow for dynamic effects that captivate audiences. The instrument’s flexibility also makes it an essential component of marching bands, film scores, and even pop music arrangements.
 When you hear the warm, velvety voice of a French horn, it’s hard not to be captivated. But have you ever wondered why this brass instrument is considered one of the most challenging yet rewarding to play? Its distinct tone — both rich and mellow — comes from a combination of Embouchure control, air flow, and the intricate design of its rotary valves. The French horn isn’t just another instrument; it’s a bridge between technical mastery and musical expression.
When you hear the warm, velvety voice of a French horn, it’s hard not to be captivated. But have you ever wondered why this brass instrument is considered one of the most challenging yet rewarding to play? Its distinct tone — both rich and mellow — comes from a combination of Embouchure control, air flow, and the intricate design of its rotary valves. The French horn isn’t just another instrument; it’s a bridge between technical mastery and musical expression.
The mechanics of brass instruments are on full display in the French horn. Its long, coiled tubing and flared bell create a unique resonance, while the player’s lips produce air vibrations that travel through the horn’s cylindrical chamber. Controlling pitch and tone requires precise Embouchure adjustments and careful management of air flow, making it an instrument that rewards patience and dedication.
The French horn comes in several types, each suited for specific musical contexts:
Mastering techniques such as overblowing, tone variation, and register adjustment allows horn players to navigate intricate orchestral passages and deliver expressive solos.
From the baroque orchestra to contemporary ensembles, the French horn has played a vital role in shaping orchestral sound. Its ability to blend seamlessly while also standing out in solos has made it indispensable in symphonies, film scores, and jazz arrangements. Legendary horn players have elevated its status, demonstrating that this lip-vibrated instrument is both a technical challenge and a canvas for creativity.
 Have you ever wondered what anchors the bold harmonies of an orchestral brass section? That deep, resonant foundation comes from the tuba, the largest and lowest-pitched of the brass instruments. Its rich sound supports ensembles, providing both power and stability while allowing other instruments to shine. But playing the tuba is far more than blowing into a big tube — it’s an exercise in breath control, precision, and musicality.
Have you ever wondered what anchors the bold harmonies of an orchestral brass section? That deep, resonant foundation comes from the tuba, the largest and lowest-pitched of the brass instruments. Its rich sound supports ensembles, providing both power and stability while allowing other instruments to shine. But playing the tuba is far more than blowing into a big tube — it’s an exercise in breath control, precision, and musicality.
The tuba operates on the same basic mechanics of brass instruments: air vibration created by the player’s lips through a mouthpiece. The instrument’s long, coiled cylindrical chamber amplifies these vibrations into deep, full-bodied tones. Valves and slides adjust the tube’s length, giving players remarkable pitch control across the harmonic scale. Because of its size, mastering Embouchure and air flow is essential to produce smooth, consistent sound.
Tubas come in several varieties, each serving different musical needs:
Each variant offers unique challenges and rewards, from sustaining long notes to executing expressive passages with precision.
From classical symphonies to modern jazz ensembles, the tuba anchors the harmonic structure while allowing the ensemble to explore dynamic musical expression. Its ability to blend yet stand out is what makes it indispensable in orchestras, concert bands, and brass ensembles alike. Techniques like tone variation and careful register adjustment allow tuba players to create both subtle warmth and commanding presence.
Have you ever wondered which brass instruments bridge the gap between the bright brilliance of the trumpet and the deep foundation of the tuba? Enter the euphonium and baritone horn — two instruments celebrated for their rich, mellow tones and versatility in both ensembles and solo performances. Often referred to as the “cellos of the brass family,” they bring warmth, expressiveness, and technical finesse to any musical setting.
Both the euphonium and baritone horn rely on air vibration through a cylindrical chamber and careful Embouchure control to produce smooth, resonant sound. Valves and slides allow for precise pitch control, while air flow management ensures a full, consistent tone across the harmonic scale. Though similar, each instrument offers a distinct feel:
These instruments are beloved for several reasons:
From brass band classics to contemporary music, the euphonium and baritone horn add depth and color. Players who master Embouchure control and tone variation can express subtle musical nuances, making each performance uniquely compelling.
 Have you ever wondered which brass instruments fill the sweet spot between the bright brilliance of a trumpet and the deep resonance of a tuba? That’s where the euphonium and baritone horn come in — instruments celebrated for their warm, lyrical tones and versatility across ensembles and solo performances. Often called the “cellos of the brass family,” they combine musical expression with technical agility, offering a uniquely satisfying playing experience.
Have you ever wondered which brass instruments fill the sweet spot between the bright brilliance of a trumpet and the deep resonance of a tuba? That’s where the euphonium and baritone horn come in — instruments celebrated for their warm, lyrical tones and versatility across ensembles and solo performances. Often called the “cellos of the brass family,” they combine musical expression with technical agility, offering a uniquely satisfying playing experience.
Both instruments rely on air vibration through a cylindrical chamber and the player’s Embouchure to produce their characteristic smooth, resonant tones. Valves and slides allow for precise pitch control, while careful air flow management ensures each note carries with clarity. Here’s how they differ:
These instruments are cherished for several reasons:
From traditional brass bands to contemporary orchestral works, the euphonium and baritone horn bring depth and nuance. Mastery of tone variation and Embouchure control allows players to express subtle musical emotions, making each performance memorable.
While the trumpet, trombone, and tuba often steal the spotlight, the world of brass instruments is full of hidden gems waiting to be explored. Have you ever heard of the flugelhorn, cornet, or ophicleide? These lip-vibrated instruments may be less common, but they bring unique textures and colors to music, offering players exciting opportunities for musical expression.
Let’s explore some of the lesser-known members of the brass instruments list
With so many brass instruments to explore, how do you decide which one suits you best? Whether you’re drawn to soaring melodies, deep harmonies, or expressive solos, the right instrument can make learning enjoyable and fulfilling. Let’s break down the key factors to help you make an informed choice.
Tips for Beginners
Choosing the right instrument is the first step toward a rewarding musical journey. If you’re ready to explore your options, you can start with an Online Instrument Course or book a trial class to discover the instrument that speaks to your musical soul.
Exploring the world of brass instruments opens up a universe of sound, technique, and musical expression. From the bright, commanding trumpet to the deep, resonant tuba, each instrument offers a unique voice and a distinct way to connect with music. Have you felt the excitement of imagining yourself mastering the smooth slides of a trombone or the warm, lyrical tones of a French horn?
Choosing the right instrument is more than picking a sound — it’s about discovering the one that inspires you to practice, perform, and create. Whether you’re drawn to bold fanfares, expressive solos, or harmonic depth, understanding the mechanics of brass instruments, the role of Embouchure, and the magic of air vibration can guide you toward the perfect fit.
Every brass instrument, from the familiar to the lesser-known, holds the potential to transform your musical journey. So, are you ready to take the next step? Dive into learning through an Online Instrument Course or book a trial class and experience firsthand the joy, challenge, and artistry that come with mastering these incredible lip-vibrated instruments. Your brass adventure awaits — let your music speak.